How do Drones Work and What is Drone Technology?
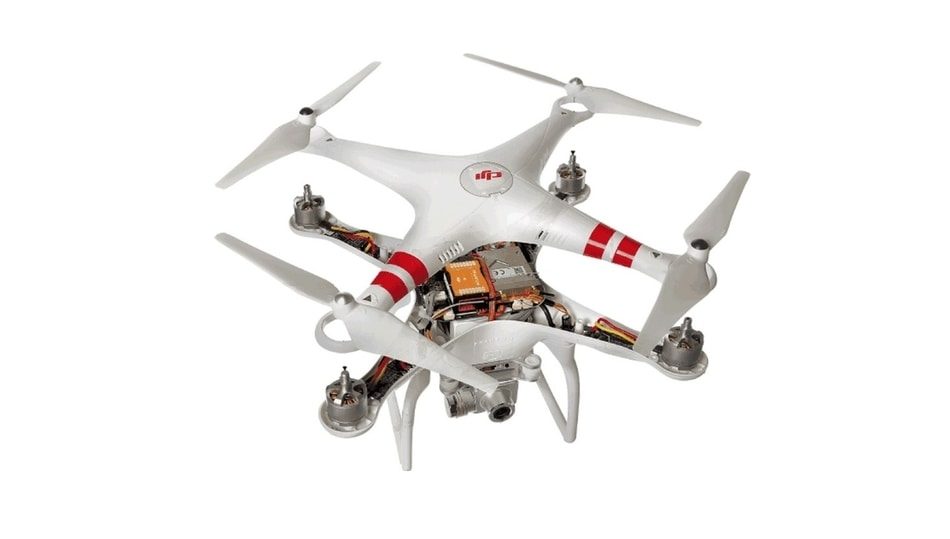

This article will explain in simple terms what a drone is and how do drones work. In the last 20 years, (UAV) drone technology is constantly evolving with a lot of new innovations that are driving the advancement of drones, and new models which are released every few months.
Below, we will discuss the latest drone (UAV) technology using the example of the most popular and advanced drones on the market. Keep in mind that most drones have very similar systems on how they operate. Drone technology covers everything about drones, from drone aerodynamics and materials of manufacture to the sensors, circuit boards, frames, chipset, and software that are the brains of the drone.
DJI is certainly the most famous brand for drones in the world and has the largest share in the open market. Even Hollywood uses DJI drones for recording movies, as do famous influencers around the world. The most famous DJI drone is certainly the DJI Phantom 4 Pro.
DJI Phantom is the best example of how we can describe modern UAV technology. This drone has almost everything it needs to meet market standards, such as a gimbal, motion sensors, Return to Home option, easy to fly mode, etc. Every year we can see the new drone models on the market, with new features. In 2021 DJI introduced the DJI FPV model, which blew everyone in the drone industry and set the new standards.
Innovation in UAV drone technology is evolving at a rapid pace. So it is important to keep up with the drone market. In this article, we’ll cover everything about drone technology and how do drones work. So let’s start with the basics.
How Drones Work
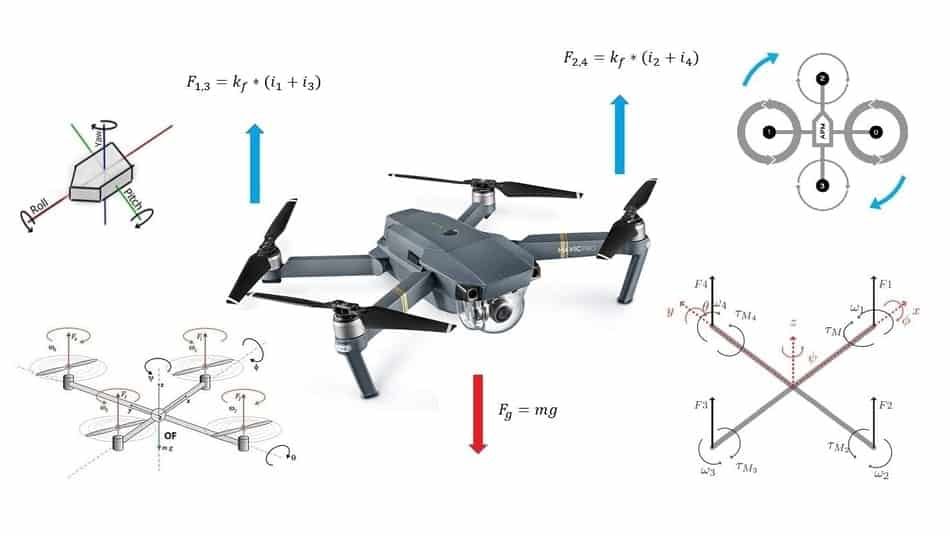
The drone is a “remotely piloted aircraft” (RPA) that have no pilot on board. They are also classified as remotely piloted systems (RPAS). Some types of drones are controlled with an app on the tablet, smartphone, or computer, while others are controlled by a remote controller.
Drones work by using their rotors, which have propellers that are attached to a motor, which allow the drone to hover. When these rotors spin together, they are pushing the air down and the air pushes back up on the rotors. That way, the drone lifts up into the sky and flies.
The drones can work mainly in two ways:
- Piloted by the pilot using the remote controller that allows the drone to be guided in real-time.
- Not Piloted, in this case, they perform their task independently (after programming the “on-board computer” or with remote control via software)
Before losing the signal (on remote controller), professional drones can reach up to 3 km (1.8 mi) distance, while low-budget drones have a much lower range. Similar considerations can also be made for autonomy: generally, low-budget drones can fly for a few minutes (10-15 for medium-low range drones), but the flight duration of a professional drone can even reach 40 minutes.
A typical drone (UAV) is constructed from lightweight composite materials so they can reduce weight and improve maneuverability. The strength of the composite material allows military drones to fly at extremely high altitudes.
Most drones are equipped with a variety of modern technologies such as infrared cameras, GPS, sensors, night vision modes, etc. The drones are controlled by Ground Control Systems (GSC), that is also known as a ground cockpit.
If you want to know more about how do drones work, you can read Physics Behind How Drones Fly article!
What Is A Drone & UAV Technology
Drones or UAVs are designed with the ability to fly in the air without a pilot. Below we will get through the latest drone technologies and how they operate. Therefore, we’ll provide you with plenty of information on their working principle and the technology that are available on the market.
On the internet, there are many links that you can follow to explore new types of components that drones have. Here you have an awesome and complete guide about drone parts and components: Drone Parts And Components Overview With DIY Tips. So let’s start!
Complete list of technology that drones use today:
| Drone Technology: | Drone Technology: |
|---|---|
| 1) Drone Types And Sizes | 15) Smartphone App With Ground Station Function |
| 2) VTOL (Vertical Take-Off & Landing) Drones | 16) High Performance Camera Drones |
| 3) Return Home & Radar Positioning | 17) Drones With Zoom Cameras |
| 4) Obstacle Detection And Collision Avoidance Technology | 18) Gimbal Technology |
| 5) Gyro Stabilization, IMU And Flight Controllers | 19) Creating 3D Maps With Sensors |
| 6) Drone Motor Direction & Propeller Design | 20) Video Editing Software |
| 7) No-Fly Zone (NFZ) Technology | 21) Operating Systems In Drone Technology |
| 8) Ready to Fly Mode (GPS) Drone Technology | 22) Security And Hackability of Drones |
| 9) Internal Compass & Fail-safe Function | 23) Latest Innovative Technology of Drones |
| 10) First Person View (FPV) Mode Drone Technology | 24) Smart Flight Systems |
| 11) Firmware Software | 25) Drone Application |
| 12) LED Flight Indicators | 26) Learning to Build And Program Drones |
| 13) UAV Remote Control & Receiver System | 27) Drone Battery Management System |
| 14) UAV Range Extender Technology | 28) Low-Noise Drone Props |
1) Drone Types And Sizes
There are so many varieties of drones that can be easily found around and they all serve different applications; therefore it is difficult to define a common criterion of comparison. But all of them work on the same principle and use the same drone technology. Depending on the need or application, they can vary in size and design. One of the largest drones is the Predator drone, and it is used for military purposes.
There are 2 types of drones:
- Rotor drones
- Fixed-wing drones
Rotor drones can be divided on: Tricopter, Quadcopter, Hexacopter, and Octocopter. These models are generally controlled by specially designed brushless DC motors.
These drones, in addition to being able to fly, can also hover in place. Also, the size and class of these drones vary from mini drones, racing drones, commercial drones to professional models that are used for business.
Fixed-wing drones are drones with quite unique designs compared to the commonly used types of multi-rotor drones. These drones are unable to stay stable in the air as they are not very powerful to combat gravitational force, and don’t have vertical take-off.
They find their applications and they are used to cover large areas, and their flight time depends on their battery system. These types of drones are much less on the market as opposed to rotor drones.
2) VTOL (Vertical Take-Off & Landing) Drones
In simplified terms, VTOL drones take off “like a helicopter” by the use of motors that have attached propellers and then move “like an airplane”. Some VTOL drones are quadcopters, but not all. Such devices have the indisputable advantage, like helicopters, they do not require a runway or launching catapult for takeoff and a parachute for landing. Almost every drone must have this technology built-in.
The concept for these drones is that they have unique fixed wings for long-distance and are capable to do high-speed flights. These drones are used to deliver drugs and medical equipment to remote areas or even from one urban hospital to another. The problem is that helicopters and planes are expensive and that pilots are rare.
3) Return To Home & Radar Positioning
Most of the latest drones that are on the market are equipped with Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) such as GPS and GLONASS. There are 2 ways to fly drones: in GNSS mode or in non-satellite mode. Most DJI drones can fly in P-Mode (that includes GPS & GLONASS) or in ATTI mode, which does not use satellite navigation. The drone must use GPS in order to return home (it’s starting position).
High-precision navigation is very important when flying, especially if the drone is used for 3D mapping, terrain surveying and Search & Rescue missions. GNSS signal is determined by 3 factors: the inclination angle of the satellite, the altitude of the orbit, and the Earth ground-level ‘field of view’.
To understand the GNSS, you need to know that each satellite is transmitting only 2 pieces of information: Its position in space, and its clock time. When you turn your drone for the first time, the quadcopter is searching for GNSS satellites.
Basically, a satellite constellation is a group of satellites that are working in synchronization and providing coordinated coverage.
UAV Drone GNSS
On the remote controller, the radar technology will give the following signal;
- Detection of a number of GNSS satellites and its readiness to fly
- Giving the position and the location of the drone
- Signaling the low battery level, at which the drone will fly back to the starting point
- Loss of transmission between the remote controller and the drone when it returns to the starting point
- Fixing the starting point for “Return to home” function
4) Obstacle Detection And Collision Avoidance Technology
Drones with obstacle detection and collision avoidance sensors are increasingly popular in the consumer and professional sectors. This obstacle detection and avoidance technology started with sensors that are able to detect objects in front of the drone. Such systems scan the environment, and then the software algorithms with SLAM technology make it into 3D maps, allowing them to detect and avoid objects.
The different drones use the following obstacle avoidance sensors, alone or in combination;
- Stereo vision.
- Ultrasonic (sonar).
- Flight time.
- Lidar.
- Infrared.
- Monocular vision.
The DJI, which is the leading consumer and professional drone maker on the market, is leading the way in this technology. The DJI Mavic 2 Pro and Mavic 2 Zoom have some of the best obstacle avoidance systems. They have 6 obstacle detection directions and 4 obstacle avoidance directions, which is exceptional and very impressive.
Keep in mind that every drone is different, while the more expensive drones that are used for commercial inspections, photogrammetry, and filmmaking already have those sensors built into them. This drone technology is very popular today.
For the drone owner, it is very easy to get carried away in flight. If you lose your bearings or focus, you could easily fly backward or sideways into an object. With obstacle detection technology and the many other safety features that drones have, we should see many more people getting into the drone world as a hobby or a profession.
5) Gyro Stabilization, IMU And Flight Controllers
The gyroscope stabilization technology is used to help the drone to fly unmanned. So its main task is to provide complete navigation to the central flight controller. Also, the gyroscope is useful for measuring the rate of change of an angle. It can be measured along 3 axes. Some iteration is needed to get the angle. The axis of rotation of the sensor must coincide with the axis of the UAV.
An Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is an electronic component that measures sensor acceleration, angular velocity, and orientation using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers. The IMU then detects changes in the rotation of a drone such as pitch, roll, and yaw where it uses one or more gyroscopes.
Keep in mind that IMU allows a GPS receiver to function and operate when GPS signals are not available, in cases where you are in tunnels, inside buildings, or when there is electronic interference.
A flight controller is nothing more than an electronic board that controls the operation of the drone. If you want the drone to move in a certain direction, all you have to do is turn on the controls, and then the electronic board will similarly control the motors of the device. This is actually the “brain” of a drone.
Since the controller comes with a large number of sensors, it can give us accurate position information and other information about the drone in the air.
6) Drone Motor Direction & Propeller Design
In order for the drone to hover, it is necessary that the total thrust of all four motors that are lifting the drone is equal to the force of gravity that pulls it down. On a drone (quadcopter) the motors and propellers work in pairs. That means that 2 motors are rotating clockwise (CW) and 2 motors are rotating counterclockwise (CCW). This is called a “zero torque effect”.
So there are four forces that interact with the drone and without which it cannot fly:
- The drag which corresponds to the force which opposes the displacement
- The lift which corresponds to the force that pushes the drone upwards
- The tractionon which corresponds to the force which moves the drone forward
- Gravity, which is the force that attracts the drone to the ground
Keep in mind that large propeller designs are in some cases less effective operating at the axial velocity. On the other hand, the most efficient propeller designs are those which maintain a pitch to diameter ratio of 1:1.
7) No-Fly Zone (NFZ) Technology
In order to guarantee the safety of flights carried out in risk areas, DJI has integrated limited or no-fly zones around the world. These areas are most sensitive, for example airports, prisons, military sites, etc. You will not be able to take off near some of these areas or enter them when you are flying. This drone technology is built into the drone itself.
Indeed, these DJI NoFlyZones are programmed in your drone and updated regularly. This prevents your drone from entering one of these areas. That zones are available on the DJI website , where you will find a map with different areas that are categorized. Some of these zones are:
- Recommended flight zone: this zone is recommended for safe and unrestricted flight
- Restricted area: An area can be restricted to secure a dangerous site such as a prison.
- Warning zone: You will receive an alert message notifying you of a warning zone,
- Authorization zones: These zones appear in blue on the map of the DJI GO or DJI GO 4 applications.
8) Ready to Fly Mode (GPS) Drone Technology
To have your drone in “Ready to Fly” mode you need to calibrate your compass. For that, the drone needs to search the location of the GPS satellites. When there are more than 6 satellites found, the quadcopter enters the “Ready to Fly mode”. This process is performed by compass calibration on a drone align the drone’s flight system with the Earth’s magnetic north. This process takes only several minutes.
9) Internal Compass & Fail-safe Function
The internal compass function allows the drone and the remote control system to have the exact location where the drone is in flight. This process of calibrating the compass is necessary if you want to establish a reference point.
The starting point is the location where the quadcopter will return if he loses a signal between the remote control system and the drone. This is also called the “fail-safe function”. That’s why we in Drone Tech Planet think it is important for you to know how this function works and that it is part of drone technology.
10) First Person View (FPV) Mode Drone Technology
Flying a drone with FPV can literally feel like a bird. FPV in the field of a drone is that you are broadcasting the video in real-time from the camera of the drone to the monitor, goggles, or helmet of the pilot. This technology was developed to enable the pilot to view the trajectory of the drone in real-time with his own eyes.
To use the FPV with a drone, a camera, video transmitter, and antenna are installed on the drone. The principle of operation of such a device is as follows – a built-in camera broadcasts video in real-time directly to the screen of your smartphone, special glasses, or a helmet. Accurate transmission is carried out by a video camera, transmitter, and antenna.
FPV Pros:
- precise orientation on the terrain and in the position of the drone;
- the quadcopter can fly longer distances;
- completely different sensations are experienced than during normal flight;
- massive use in the entertainment industry.
The transmitter and receiver built into the quadcopter are capable of operating at a wide variety of frequencies, ranging from 900 MHz to 5.8 GHz. Drones operating at 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz are widespread. To implement FPV flight, the pilot needs either a remote control with a monitor and a receiver or glasses with a built-in receiver.
FPV is extremely useful for photographers, videographers, and of course “drone racers”. At the moment FPV is very fashionable. Manufacturers are increasingly offering this system to new buyers. The DJI has released one of the best FPV models on the market in 2021, the DJI FPV. Check it out!
11) Firmware Software
A drone is a flying computer that has an attached camera and sensors on it. Firmware is software that controls the operation of that computer (hardware) on a device. Without firmware, most electronic devices, like drones can’t work; and thanks to firmware, the device performs its functions. Most manufacturers release firmware updates for their drones on a regular basis, while providing the necessary software to write new firmware.
Basically, the purpose of a firmware update is to fix, adjust, add new features and in rare cases reveal, previously hidden potential. Like smartphones and computers, drones have firmware that is communicating with physical components of the drone and remote controller.
12) LED Flight Indicators
Every commercial drone, mini drone, racing drone, and even professional drone needs to have the LED light indicators. These lights are usually located at the front and back of the drone. They can be green, red, and yellow (this has become the UAV standard). The frond LEDs indicate where the drone is in the air, while the red LEDs show the status of the drone, such as firmware update and flight.
Knowing which LED light is for what is important lets you know what the drone is reporting. If you notice slowly flashing red LED, it means that the battery level on your drone is low, while the solid red light indicates an error. The meaning of these indications comes to you on the manual sheet that comes with the drone.
13) UAV Remote Control & Receiver System
To fly with your drone you will need a receiver. Every drone has one installed. But for more complex drones, the transmitter is not provided automatically. You must therefore buy it yourself, and this is what will allow you to take a step forward in terms of quality and efficiency. The receiver will indeed determine the range, performance, etc.
For a drone, it is necessary to obtain a quality radio control, compatible with this transmitter. The receiver will simultaneously receive the signals from the various controls (the channels). He is able to differentiate them and to reassign them to the action which falls to him. his receiver can receive up to eight different instructions, which gives more precise control to the drone.
14) UAV Range Extender Technology
The range of a drone depends on numerous limiting factors, starting with the maximum range of the radio signal that connects the controller to the receiver on board and vice versa. The UAV range extender is a device that increases the strength of a communication signal that typically operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency to make a drone reach a great distance.
The effectiveness of a range extender depends on its quality. Basically, there are two common frequencies used for drones, which are 2.4GHz and 1.2GHz. Each range extender will allow you to pump the flight range and video signal transmission of quadcopters like DJI Mavic 2 Pro and DJI Spark.
Owners of the DJI Mavic Pro and DJI Spark drone often wish to extend the range of their drones. According to the technical documentation, the maximum range of the DJI Mavic Pro video signal transmission is only 2.17 miles (3.5 km).
Many older models don’t fly far, that is why range extenders are needed. Various interference, obstacles, power lines, Wi-Fi and mobile towers greatly affect the range of your drone. So, for example, in urban conditions very often the flight range does not exceed 0.62 miles (1 km).
15) Smartphone App With Ground Station Function
Many new drones have the ability to be controlled from a smartphone app. These apps can be easily downloaded from Apple Store or Google Play in just a few clicks.
Although this is more for mini drones and selfie drones because they are very simple and portable. But this is not the case for professional drones that require much more advanced options than basic applications have. With the smartphone app, you have full control over the drone.
16) High Performance Camera Drones
Equipped with high-definition photo equipment and piloted by professionals, the drone can produce breathtaking and high-quality aerial shots. That is why it is important to have a high-performance camera installed on a drone.
For a long time, good image quality was often synonymous with heavy and bulky quadcopters (and reserved for experts), but in recent years, “consumer” drones have gained the quality of their cameras grow steadily and the most recent models increasingly border on excellence. These new models can capture 4k videos and can take 20MP footage.
Earlier drone models didn’t have nearly quality cameras as they have today. There are many models and types of drones on the market capable of filming very good quality videos, but aerial photography requires paying special attention to the sensor that equips the on-board camera. When it comes to drones like DJI Phantom 4, Mavic Pro 2, DJI Inspire 1, they set the standard for today’s aerial photography.
If there is one drone that has changed the landscape of aerial filmmaking, it is DJI’s, Inspire 2. Among the features of the Inspire 2, a dedicated FPV camera allows the operator to have a personal flow, leaving him free to operate the cinema camera independently. This drone is even used in Hollywood.
The base DJI Inspire 2 model has a 1-inch, 20 MP sensor on the Zenmuse X4S gimbal camera. This is one of the most powerful drones currently in the catalog of the Chinese manufacturer. Capable of filming in 5.2K in CinemaDNG RAW, it has an autonomy of 27 minutes and can fly at the maximum speed of 94 km/h.
17) Drones With Zoom Cameras
Only a small number of drone manufacturers make drones compatible with cameras that offer the ability to zoom. Whether you are an aerial photographer or a photojournalist, having a drone with the ability to zoom will definitely expand your video capture possibilities. These cameras entered the market in 2016.
There is no doubt that using drones in place of people to perform visual inspections of tall (and hard to reach) buildings is much safer with using the zoom option on the camera. It is no longer necessary to approach with your drone very close to the areas you want to film. Zoom cameras are capable of taking detailed close-ups of structures even 656 ft (200m) away from the target.
Chinese company DJI release the revolutionary Zenmuse Z30 camera in October 2016. This camera has 30x optical zoom and 6x digital zoom. After that, more and more manufacturers began to incorporate zoom cameras into their drones.
DJI has introduced Mavic 2 Zoom that specializes in zooming. The DJI Mavic 2 Zoom has the integration of a 24-48 mm (x2) optical zoom, a first in the drone industry. Equipped with a more classic 1 / 2.3-inch sensor, this optical zoom is supplemented by a digital zoom x2, allowing remote pilots to obtain a large zoom range.
The DJI Mavic 2 Zoom also highlights Super Resolution, which is based on capturing 9 shots with the 48mm telephoto lens.
18) Gimbal Technology
The purpose of the gimbal is to keep your camera at the same angle regardless of the movement of the drone by using calibrated and often remotely controlled electric motors. This is the fascinating drone technology that we have in UAVs.
Therefore, having a gimbal on your drone is very important if you plan to take high-quality aerial photos, videos, or 3D images. Also, it is important to properly balance the lens in the gimbal to make the most of the video stabilization.
The advantage of purchasing a camera gimbal through the manufacturer of your drone is that you are going to get support for your device as well as a lot of easy-to-find documentation on how to use and maintain your gimbal. Most drones today have built-in gimbals on their drones.
19) Creating 3D Maps With Sensors
3D mapping, also known as photogrammetry, is the science of calculating distances from photographs. The result of photogrammetry software is usually a 3D map, 3D image, or 3D model of some real-world object or piece of land.
LiDAR Technology has proven to be effective in providing accurate aerial photography and uses fast laser pulses to create a 3D model. LiDAR is great solution when you need to get high-resolution displays of the earth’s surface.
Drones that use Time-of-Flight (ToF), appeared on the market in 2016. Those cameras use LiDAR sensors to perform a variety of functions such as object scanning, obstacle avoidance, confined space navigation object tracking, height measurement, 3D shooting, etc.
Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras that use LiDAR sensors have a big advantage over other technologies because they can measure distances to objects much easier. Drones are using autonomous navigation and can be programmed to fly over a specific area using GPS and create a photogrammetric mapping using LiDAR. The camera is capable to take photos at 0.5 or 1-second intervals.
DJI’s Zenmuse L1 is the first DJI Surveying Solution with Lidar. The Zenmuse L1 combines a powerful yet lightweight Livox lidar module (70° field of view) with a high-precision IMU and a 20MP photo camera equipped with a 1-inch CMOS sensor on a 3-axis stabilizer.
Today we have many software solutions for 3D photogrammetry, and this allows you to pick the one that best suits you and your needs. DroneDeploy is certainly one of the best 3D mapping software in the world right now. They have their own mobile app and live maps that are used in a variety of sectors to create 3D maps.
When you capture high-quality footage with your drone, it is very important to use the best photogrammetry software so you can process those images into real maps. Here we will list the 10 best software systems for drone-based photogrammetry, 3D mapping and modeling. Many of these photogrammetry software solutions work with both ground and drone imagery.
- DroneDeploy 3D Mapping Mobile App
- Photogrammetry software Pix4D Mapper
- DroneDeploy Enterprise 3D Mapping Software
- Photogrammetry software AutoDesk ReCap
- Orthophotography and 3D Modeling Software Maps Made Easy
- Photogrammetry software 3DF Zephyr
- Photogrammetry software Agisoft PhotoScan
- PrecisionHawk 3D Mapping Software
- Open source photogrammetry software OpenDroneMap
- ESRI Drone2Map for ArcGIS
20) Video Editing Software
Whether it is for amateurs or professionals, video editing software is essential. You want to develop the footage you took from the drone in the best possible quality and display it on your TV. The advantage of software lies in its ergonomics, ease of handling, versatility, and performance. Most drones shot in Adobe DNG RAW format. In most cases, you can use a lot of video editing software to edit your drone footage.
21) Operating Systems In Drone Technology
When it comes to software, most drones use Linux operating system, while only a few use Windows. The reason for this is that in 2014 the Linux Foundation launched the Dronecode project.
The Dronecode Project is mostly the open source project that gives the existing UAV project that is on non-profit structure on the Linux Foundation. Drone technology is not only hardware but also the software of the drone.
22) Security and Hackability of Drones
It is clear that drone manufacturers are trying to somehow protect their devices from interception. But this is far from possible, especially if real experts (Hackers) in their field take up the matter. The situation is aggravated by the fact that even the most advanced drones are equipped with the simplest traffic encryption systems.
Recently, information appeared that a team of researchers has created a system that allows you to take control of almost any drone. Moreover, this does not require an electromagnetic gun, permission from the authorities, or anything else. It is enough to use a specially modified control panel.
The method proposed by specialists allows not only to intercept control but also to form a “digital fingerprint” that is unique for each drone. This fingerprint can be used to distinguish “our” drone from “someone else’s” and form a list of trusted systems.
I wrote an interesting article on this subject, here you can read Can Drones Be Hacked.
23) Latest Innovative Technology of Drones
The leading drone manufacturer, DJI, has many products in the professional and consumer UAV market. Here we will see the list of the newest models that have patented technologies:
- DJI Mavic Air: Drone that is equipped with 4k camera and it’s very stable in flight. It has the collision avoidance function which is useful in flight. Another interesting function is the ability to fly using hand gestures and it has facial recognition technology.
- DJI Mavic 2: There are 2 models in this series, Pro, and Zoom. It has a function to prevent a collision from all directions.
- DJI Mavic 2 Enterprise: This drone comes with zoom or thermal imager. It has integrated spotlights, beacon, and a loudspeaker. This model is used in search and rescue missions.
- DJI Phantom 4 Pro: Comes with Vision Collision Avoidance Technology. This drone has a lot of new technologies that include 4k aerial photography and photogrammetry.
- DJI Inspire 2: It has patented engines and design. Inspire 2 is used for professional 5k aerial photography, thermal and multispectral imaging.
- DJI Matrice 600: This drone is a commercial multi-copter on which is possible to mount 7 different types of Zenmuse cameras.
- DJI Matrice 200: It has IMU, dual battery, and satellite navigation system. Ability to install 2 cameras (thermal and zoom). It has the collision avoidance function from 6 directions with the ToF laser.
- Walkera Voyager 5: It has a camera with 30x optical zoom, night vision, and infrared zoom where it is possible to work in low light.
- Walkera Vitus: This model comes with anti-collision sensors that also have a low-light night vision camera.
24) Smart Flight Systems
More and more drones come with smart flight functions, halfway between programming before take-off and triggering actions in mid-flight. These functions prove to be very useful for a pilot to control a drone more easily, and allowing an automatic return to the starting point in the event of a problem, or to easily film moving subjects. Smart flight modes are very useful, especially for new pilots.
These drones have smart flight controllers that have the following modes: Active Tracking, Waypoints, Follow Me, Return To Home, etc. One of the drones that have super-smart flight modes is DJI Phantom 4 Pro. This drone has the following smart flight modes;
- Follow Me Mode
- S-Mode (Sports)
- A-Mode (Attitude)
- P-Mode (Positioning)
- Beginner Mode
- Avoiding obstacles
- Home Lock
- TapFly
- Gesture Mode
- Terrain Tracking Mode
25) Drone Application
The good thing about drones is that they are multifunctional and can be used for a variety of things. For example, if you install a camera or some sensor on your drone like LiDAR, ToF, Thermal, Multispectral, the range of applications that your drone can perform rapidly expands. Thus, drones are not only used to take photos and videos, but their application is extended to many other things. Below we will list a task of drone applications.
26) Learning to Build And Program Drones
Making your own drone is no longer a challenge. Choosing the right equipment and buying a drone KIT, will help you to build a drone in no time. Some, specialized sites, even recommend buying a drone kit, that is easy to assemble.
This can be a very simple introduction to familiarize yourself with the different components of drones. Also, it will allow you to develop a construction project that will be closer to your initial objective.
To program a drone today, you do not need to understand the physics of flight and other subtleties, since these questions have already been solved for you by the developers. Also, there are many programming languages that drones can have and that you can easily learn, such as Swift, Tynker, Python, Scratch, and Blockly. By programming the drone, you will be able to give the drone commands with which it will be able to perform tasks itself.
Related Article: Drone Vs Helicopter: What is The Difference?
27) Drones Battery Managment System
The flight time of a quadcopter directly depends on the type of drive, as well as the power source. Most consumer drones are powered by a single lithium-type battery. Batteries of this type have a large capacity and, if used correctly, last much longer than conventional batteries. This drone technology system helps drones to fly even more.
Drones now use a battery management system (BMS) that helps them to get more from the battery and to have a longer flight time. Battery Management System is an electronic system that controls the charging / discharging process of the battery, and is responsible for the safety of its operation, monitors the condition of the battery, evaluates the secondary performance data.
All existing DJI drones are equipped with Li-Polymer batteries only. The Mavic 2 Series drones are powered by Intelligent Flight smart batteries.
They are designed to fly in 27 minutes, and built-in smart functions warn you of low battery, high or low temperature, and possible malfunctions. Full details of this can be monitored online via the DJI GO app . The battery is controlled by special overload and sudden discharge protection.
28) Low-Noise Drone Props
A lot of commercial drones that are on the market are pretty noisy. It can also be irritating at times. Propellers that drones have are generally designed to have high efficiency and that is why they are noisy. Their big size, shape, weight and aerodynamics are design to maximize their flight time with appropriate thrust. Chinese company DJI used a “raked wingtip” propeller design to reduce the noise of drone. Read here Why Drones Are so Loud?
The Best Drone (UAV) Technology Videos
In the end, I will attach 2 interesting videos that describe UAV technology in detail. In this first video, you will see the amazing technology and algorithms behind drones and what they are capable to do. They talk about how they use algorithms, model-driven design to programming drones to do really interesting things. Enjoy!
Military Drones
In fact, the study of the capabilities of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in relation to military targets is just beginning. Therefore, it is not surprising that governments in many countries today are additionally investing in drones to understand what these flying machines are capable of.
Electronic flying machines that are the size of a large insect are not only a spectacular toy from a Hollywood blockbuster, but also a means of warfare. The most famous especially small drones are the Black Hornet models ranging from 1 “to 4”.
Perhaps the most famous military drones are the large aircraft of the US Army. Among the models of such drones, the MQ-1B Predator and its larger brother, the MQ-9 Reaper, should be mentioned. They are sold by General Atomics for $16.9 million apiece.
The largest and most expensive drone is considered the RQ-4 Global Hawk model manufactured by Northrop Grumman. Each copy costs $130 million, not counting the infrastructure needed to use it on the ground.

